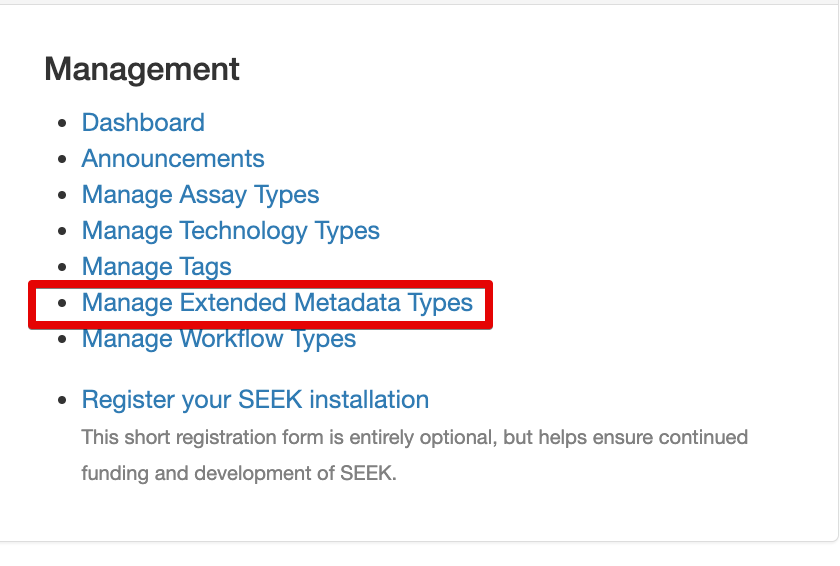
Introduction
Extended Metadata is a feature added to SEEK as part of version 1.11, originally to support MIAPPE but designed for future use. It provides the ability to define additional metadata attributes for a particular type, to support a particular standard (i.e MIAPPE).
It is not a feature a user would directly see, other than revealed through extensions that are made available:
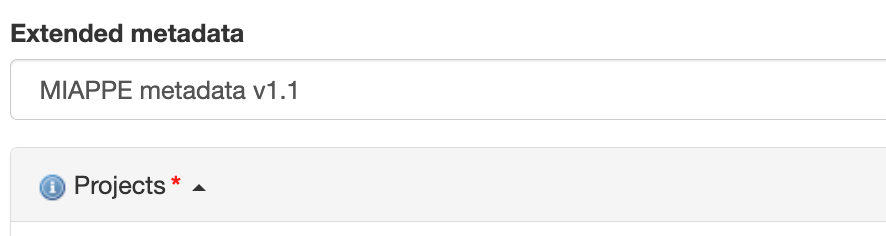
… will reveal new fields below:
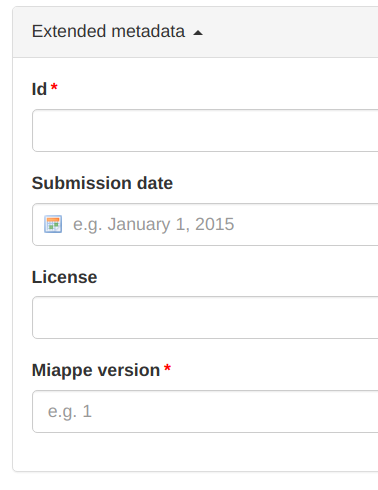
The attributes can be associated with a particular attribute type, and marked as optional or mandatory, and will be validated against. This is very similar to Samples.
Extended metadata will only be shown if defined within the database, which is currently the only way of configuring it.
How it works
Extended Metadata works in a very similar way to Samples, and shares a lot of the same code. Extended Metadata Types are defined, that describe a set of attributes with names and point to a SampleAttributeType to define the attribute type.
The Extended Metadata Type is linked to a particular resource type in SEEK. Currently, it can be incorporated into the following resource types:
ISA items (Investigation, Study, Assay), Collection, DataFile, Document, Event, Model,Presentation,Sop, Project.
You can define the supported resource type as shown below:
ExtendedMetadataType.new(title: 'person', supported_type: 'YOUR_TYPE_NAME')
Extended Metadata Type is conceptually similar to a Sample Type, as it inherits the same attribute structure. However, while Sample Types are used to create standalone Samples, Extended Metadata Types are used to augment or extend the metadata of other types (e.g., Investigations, Studies, or Assays). Instead of existing independently, extended metadata is embedded within another object, enriching its descriptive details.
This is explained in the following high level representation.
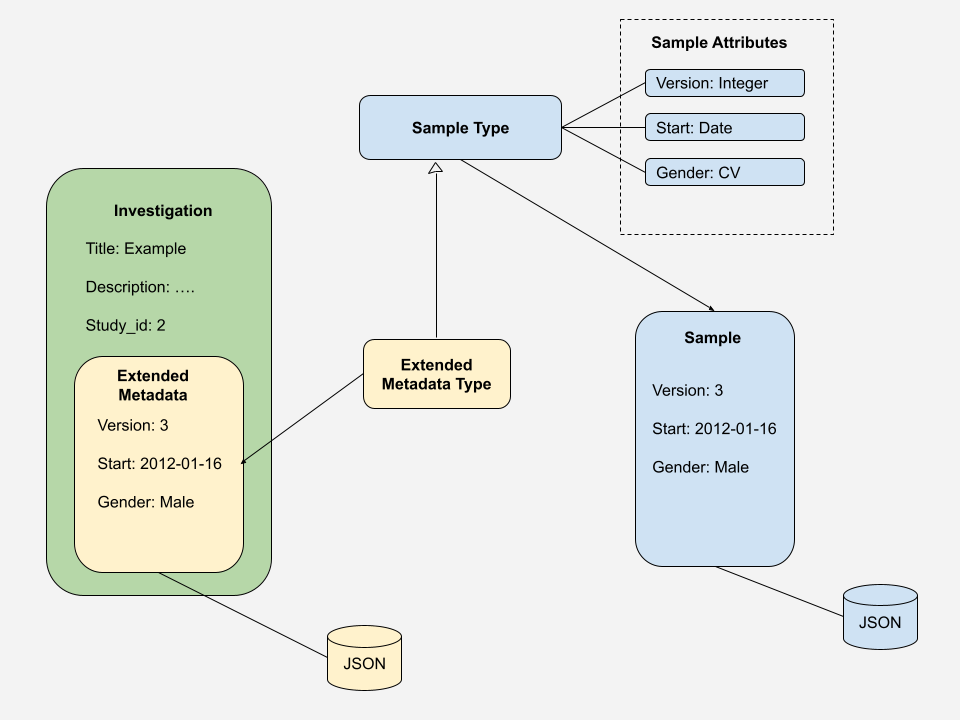
In this diagram:
Sample Type:
- Represents a blueprint used to define and create individual Samples.
- Contains attributes that describe the properties of a sample (e.g., Version, Start, Gender).
Sample:
- Samples created from a Sample Type exist as standalone entities.
Extended Metadata Type:
- Inherits the same attribute structure as the Sample Type.
- Unlike a Sample Type, it does not create standalone entities.
Extended Metadata:
- Extended Metadata created from a Extended Metadata Type.
Entity (e.g., Investigation):
- Represents the object (such as an Investigation, Study, or Assay) that holds the extended metadata.
- The Extended Metadata is embedded within this entity, enriching its existing metadata.
Creating and managing types
As a FAIRDOM-SEEK instance administrator, you have the ability to create, manage (enable, disable), and delete extended metadata types. This guide will walk you through how to perform these actions efficiently by navigating to the “Manage Extended Metadata Types” section in the Admin area.